iOS 기본 (swift)
[iOS - swift] 메모리 할당 위치 (struct, class, protocol, generic, closure)
jake-kim
2022. 6. 4. 19:17
value type, reference type
- swift에는 2가지 타입이 존재
- value type: struct, enum, collection, 기본타입(Int Double, Bool ...)
- reference type: class, function, closure
- 두 타입의 차이 - copying
- value tpye - 카피할때 데이터의 복사본을 생성
- reference type - shared instance를 생성하여 같은 인스턴스를 바라보는 참조값을 생성
- cf) value type을 사용하면, thread간 의도하지 않은 공유로부터 안전한 프로그래밍이 되어, 로버트 C. 마틴의 클린 코드에서 얘기하는 functional programming 핵심은 데이터의 불변성에 도움
메모리 공간 할당
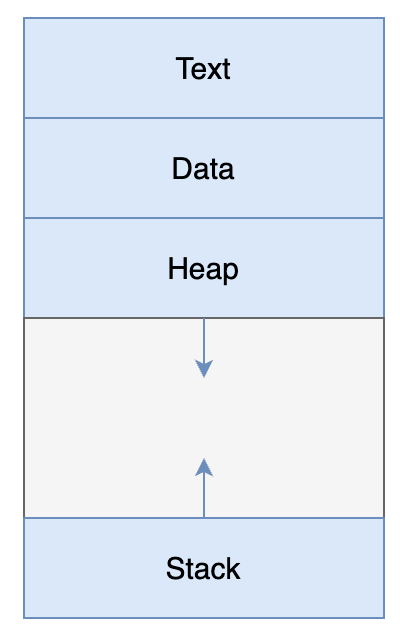
- 일반적으로 value type은 stack영역, reference type은 heap영역에 저장 하지만, struct타입이 heap에 할당되는 경우가 상당히 많이 존재
- value type의 크기가 컴파일 시간 동안 결정될 수 없는 경우 -> heap에 할당
메모리 할당
- struct가 프로토콜을 confirm 하는 경우,
- heap도 같이 저장 (3 machine words를 초과하게 되면 stack에서 오버헤드가 발생하여, 힙에 할당)
- 여기서 힙에 할당된 것들의 life cycle은 Value Witness Table에서 관리
- value type의 크기가 컴파일 시간 동안 결정될 수 없는 경우 -> heap에 할당
protocol Bar {}
struct Baz: Bar {}- value type과 reference 타입이 섞여있는 경우,
- struct B와 struct C 모두 Heap에 할당
// Class inside a struct
class A {}
struct B {
let a = A()
}
// Struct inside a class
struct C {}
class D {
let c = C()
}- Generic 타입인 경우,
- value type의 크기가 컴파일 시간 동안 결정될 수 없는 경우 -> heap에 할당
struct Bas<T> {
var x: T
init(xx: T) {
x = xx
}
}- Escaping closure captures인 경우,
- 대부분의 지역 변수가 reference로 캡쳐되지만, 일부는 stack영역에 할당
class SomeClass {
var handler: () -> Void = {}
func myFunc(completion: @escaping () -> Void) {
self.handler = completion // capture !
}
func callHandler() {
self.handler()
}
}Reference count - value type과 reference type이 혼합된 경우
- 데이터 준비
class Ref {}
// Struct with references
struct MyStruct {
let ref1 = Ref()
let ref2 = Ref()
}
// Class with references
class MyClass {
let ref1 = Ref()
let ref2 = Ref()
}- value type 내부에 reference type이 존재하는 경우,
- value와 reference가 혼합되어 있으니 모두 heap 영역에 저장
- value 타입의 count는 1이고, 내부 reference 타입은 2
- 즉 value type으로 reference type을 감싸면은 reference type이 별도로 count가 하나 더 증가되어 있음
let a = MyStruct()
let anotherA = a
CFGetRetainCount(a as CFTypeRef) // 1
CFGetRetainCount(a.ref1) // 2
CFGetRetainCount(a.ref2) // 2- 외부, 내부 모두 reference type인 경우,
- 외부 reference type은 2, 내부 reference type은 1
- 메모리 관리 관점에서 당연히, 외부 reference type만 갖고 있으면 내부 reference type을 2개 가지고 있지 않아도 되므로 내부는 1만 차지
let b = MyClass()
let anotherB = b
CFGetRetainCount(b) // 2
CFGetRetainCount(b.ref1) // 1
CFGetRetainCount(b.ref2) // 1- 외부는 reference type, 내부는 value type인 경우
- 외부, 내부 모두 refernece type인 경우와 동일
struct Val {}
class MyClass2 {
let val1 = Val()
let val2 = Val()
}
let c = MyClass2()
CFGetRetainCount(c) // 2
CFGetRetainCount(c.val1 as CFTypeRef) // 1
CFGetRetainCount(c.val2 as CFTypeRef) // 1복사 비용
- value type
- 기본 타입인 Int, Double과 같은 타입은 CPU register에 저장되고 복사할 때 RAM 메모리에 접근할 필요가 없기 때문에 속도가 빠른 장점이 존재
- struct와 같은 value type은 복사할때 스택에 할당되고, 일정의 시간이 지연
- String, array, set, dictionary와 같은 대부분의 extension이 가능한 타입은 write시에 값이 복사
- reference 타입
- 데이터를 직접 저장하지 않고 복사할 때 reference counting 비용이 발생
- 스레드 간 공유 자원에 관한 관리를 할때 비용도 발생
* 참고
https://www.vadimbulavin.com/value-types-and-reference-types-in-swift/